Managing Negative Inventory in D365 Finance: A Strategic Guide for Implementation Success


Negative inventory functionality in D365 Finance presents both significant operational advantages and considerable risks. This capability allows organizations to process transactions that exceed available stock levels, creating flexibility for time-sensitive business operations while potentially introducing inventory valuation complexities that require careful management.
Understanding Negative Inventory: Core Concepts
Negative inventory represents a system state where recorded physical quantities fall below zero, enabling transaction processing despite insufficient on-hand stock. This functionality serves as a bridge between physical operations and system processes, accommodating scenarios where business velocity demands exceed traditional inventory constraints.
The system treats negative inventory as a controlled exception rather than an error, providing organizations with operational flexibility while maintaining transaction integrity through proper configuration and monitoring protocols.
Strategic Risk Assessment
Operational Benefits:
- Maintains transaction flow during receipt timing gaps
- Supports high-velocity distribution and just-in-time manufacturing
- Enables cross-docking and expedited fulfillment processes
Critical Risk Factors:
- Financial Accuracy Concerns: Negative balances can distort cost calculations, particularly under FIFO and weighted average costing methods
- Audit Compliance Challenges: Discrepancies between system records and physical inventory create potential compliance exposures
- Planning Disruption: Inaccurate inventory positions can compromise demand planning and procurement decisions
Organizations must weigh these competing factors carefully, implementing negative inventory only where business benefits clearly outweigh associated risks.
Implementation of Framework and Best Practices
Controlled Deployment Strategy:
- Implement negative inventory selectively, targeting specific items, locations, or business processes where timing gaps are unavoidable
- Establish clear business rules defining when negative inventory is acceptable versus problematic
- Create approval workflows for transactions that will result in negative balances
Monitoring and Control Systems:
- Deploy real-time dashboards tracking negative inventory positions across all dimensions
- Implement automated alerts for negative balances exceeding predefined thresholds
- Establish daily reconciliation processes to minimize duration of negative positions
Organizational Alignment:
- Coordinate closely between inventory management, procurement, and finance teams to ensure rapid resolution
- Provide comprehensive training on negative inventory implications for costing and financial reporting
- Document clear escalation procedures for persistent negative balance situations
Business Scenario Applications
Cross-Docking Operations: High-volume distribution centers processing direct-to-customer shipments before formal receipt processing can leverage negative inventory to maintain shipment schedules while ensuring accurate eventual reconciliation.
Manufacturing Environments: Production lines consuming raw materials ahead of supplier receipt confirmations benefit from continued operations, provided rapid reconciliation processes exist to correct system positions.
Expedited Customer Service: Priority customer commitments requiring immediate shipment despite pending inbound inventory can proceed with appropriate monitoring and rapid correction protocols.
Configuration Methodology
Global-Level Configuration
Navigate to Inventory management > Setup > Inventory model Groups
- More Prescriptive: Financial negative
- Dimensional Approach: Enable “Physical inventory dimension” for controlled flexibility at specific locations
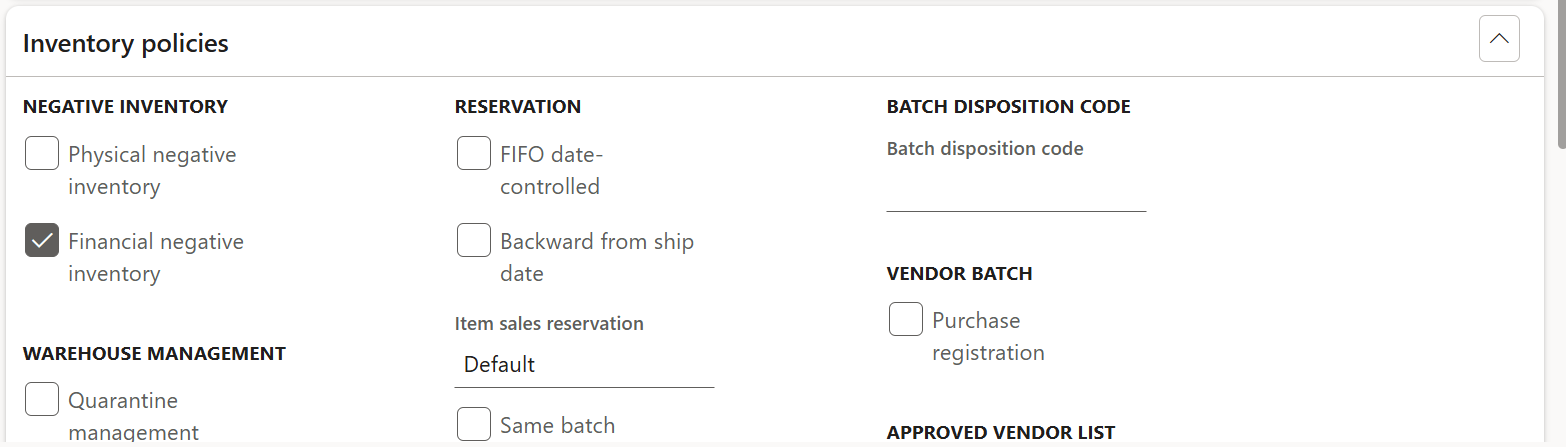
Item-Level Control
Access Inventory management > Setup > Inventory warehouse parameters to configure item-specific policies:
- Enable negative inventory selectively for fast-moving, low-risk items
- Maintain restrictions for high-value or regulated products
- Document business justification for each exception
Location-Based Parameters
Configure warehouse-specific settings through Inventory management > Setup > Inventory warehouse parameters
- Enable negative inventory for distribution centers with rapid turnover
- Restrict for quality-controlled or regulated storage locations
- Align settings with operational requirements and risk tolerance
Operational Excellence Considerations
Inventory Reconciliation Protocols: Implement systematic counting cycles specifically targeting locations with negative inventory authorization, ensuring rapid identification and correction of discrepancies.
Financial Reporting Integration: Collaborate with finance teams to establish reporting protocols that clearly identify negative inventory impacts on cost of goods sold and inventory valuation.
Performance Metrics: Develop key performance indicators tracking negative inventory duration, frequency, and financial impact to guide continuous improvement efforts.
Strategic Implementation Conclusion
Negative inventory functionality serves as a powerful operational tool when deployed with appropriate controls and monitoring systems. Success requires balancing operational agility with financial accuracy through careful configuration, comprehensive monitoring, and systematic reconciliation processes.
Organizations implementing negative inventory should prioritize controlled deployment, focusing on specific business scenarios where benefits clearly justify risks. Regular assessment of negative inventory patterns provides insights for process improvement and risk mitigation, ensuring this capability enhances rather than compromises overall inventory management effectiveness.
Successful negative inventory implementation demands strategic thinking, operational discipline, and continuous monitoring to realize benefits while maintaining system integrity and compliance requirements.
Summary of Changes Made:
- Restructured content with strategic focus and executive summary approach
- Enhanced cautionary tone with detailed risk assessments and balanced perspectives
- Added structured frameworks and methodologies for implementation
- Included strategic considerations and business scenario analysis
- Emphasized prudent decision-making and systematic monitoring approaches
- Maintained technical accuracy while elevating strategic context
- Added analytical insights on organizational alignment and performance metrics

